Mosfet Transistor Circuits Circuit Diagram MOSFETs are the most common transistors used today. Support on Patreon: https://patreon.com/baldengineerThey are switches that can be used an Arduino, Beagl
How to Use MOSFET as a Switch. To use a MOSFET as a switch, you need to ensure that the gate-source voltage (Vgs) is higher than the source voltage. When the gate is connected to the source (Vgs=0), the MOSFET remains off. Take the IRFZ44N, a "standard" MOSFET, as an example. This MOSFET only turns on when Vgs ranges between 10V and 20V. Used in automobile sound systems and in sound reinforcement systems. Conclusion. A complete beginner's guide to introduction of MOSFET. You learned the structure of a MOSFET, different types of MOSFET, their circuit symbols, an example circuit using a MOSFET to control an LED and also few areas of applications.

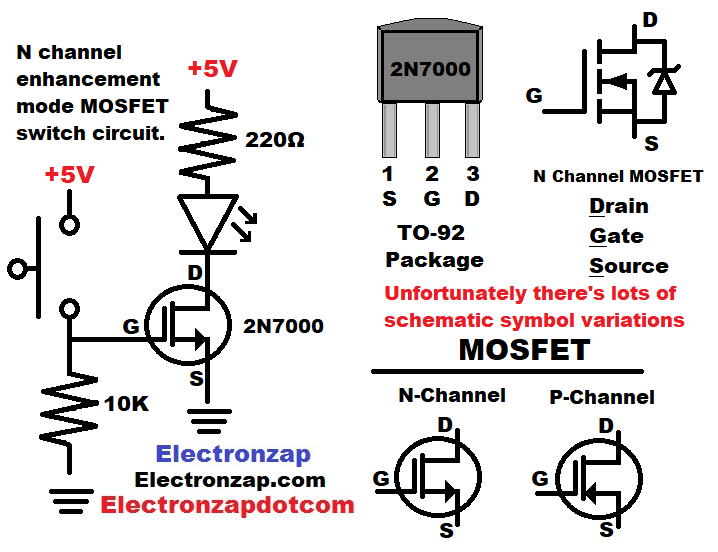
MOSFET Circuits Circuit Diagram
The final MOSFET gate circuit looks like the below figure. The gate of a MOSFET does not normally draw any current (apart from the small leakage current), but when used in switching applications where it should be turned on and off quickly, the gate capacitance has to be charged and discharged rapidly.

By using MOSFETs in inverter circuits, engineers can design power-efficient systems that meet the requirements of various electronic devices. Components Required for an Inverter Circuit. An inverter circuit is commonly used to convert DC power to AC power, enabling the use of electronic devices that require alternating current.

based circuit diagram for an inverter
Early MOS digital circuits were made using p-MOSFET. But with the advancements of microelectronics technology the threshold voltage of MOS can be controlled and an MOS technology becomes dominant, as the majority carries of n-MOS, i.e electrons are twice faster than the holes, the majority carriers of p-MOS, so the inverter circuits also using n-MOS technology until CMOS technology arrived. The operation of the enhancement-mode MOSFET, or e-MOSFET, can best be described using its I-V characteristics curves shown below. When the input voltage, ( V IN) to the gate of the transistor is zero, the MOSFET conducts virtually no current and the output voltage ( V OUT) is equal to the supply voltage V DD.So the MOSFET is "OFF" operating within its "cut-off" region.
